
Here are some suggested key books to get you started. To access the full range of books, search the Library.
Prepare for your search
CINAHL® Complete. Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature provides an index (list) of nursing & allied heath research publications . Many records have full text added to the record. CINAHL Complete contains:
Use the tabs to find out about the tools available in the software that will help you locate the articles you need.
Boolean searching is probably the most important and widespread method that can be used to search for articles databases.

Search 1. The researcher wants to know about programs that assist teenagers to stop smoking.
This is a more complex example of a Boolean search that uses several [OR] searches first then [AND] is used last to create a focused search.
Each search is retained in the 'Search History'
1. Concept 1. Search “health promotion” [OR ] “health education” (inverted commas are optional)
2. Concept 2. Search adolescent [OR] adolescence
3. Concept 3. Search smoking cessation
4. Lastly combine all three of the above searches with [AND].
The search can be written as one sequence, where brackets group the synonyms and ensure that the search is carried out in the correct order. In other words:
(health promotion OR health education) AND (adolescent OR adolescence) AND smoking cessation.

2. Applying filters/limiters
Applying filters/limiters at the end of the search is recommended.
The best method is to use the edit search button and use all useful limiters on the screen.
Alternatively use the left hand filters panel although not all filters and limiters are available.


3. Apply truncation/substitution (these tend to increase the numbers of your search results.)
3.1 The wildcard (Substitution) is represented by a ?or # in CINAHL.
For example, type ne?t to find all citations containing neat, nest or next.
Use the # wildcard in places where an alternate spelling may contain an extra character. For example, type h#ematology to find all citations containing haematology or hematology.
3.2. Truncation is represented by an asterisk (*). To use truncation, enter the root of a search term and replace the ending with an * (asterisk).
For example, type nurs* to find the words nursing, nurses, nurse, or nurseries,
Also using the earlier example in Search 1: adolescen*will retrieve adolescent and adolescence.
3.3 Note: The Truncation symbol (*) may also be used between words to match any word. For example negative pressure * therapy will return results that include the exact phrase, Negative pressure wound therapy.

4.Field searching. Search for an author in the author field and/or a keyword in the title field to quickly locate a paper that you may have seen in a reference list in a textbook or possibly in another research paper.

5. Using Subject headings in CINAHL.
Each article in a database like CINAHL (and also MEDLINE) is read and assigned several subject headings. The subject headings describe the main concepts in the article. By using the subject headings your search is improved it 'standardises' variation in terminology and language . for example: hypertension or high blood pressure.
In CINAHL , Medline and PubMed there are thousands of terms available. Subject groupings are arranged hierarchically. This hierarchical organisation of subject headings is sometimes referred to as a tree. The headings can also be referred to as MESH (Medical Subject Headings).
Search 2
What is the evidence for TED Elastic stockings in preventing DVT?
Click on CINAHL headings to go to thesaurus

The CINAHL thesaurus maps DVT to Venous Thrombosis. Tick the check box, include all subheadings and search the database. The results will appear in the search history.
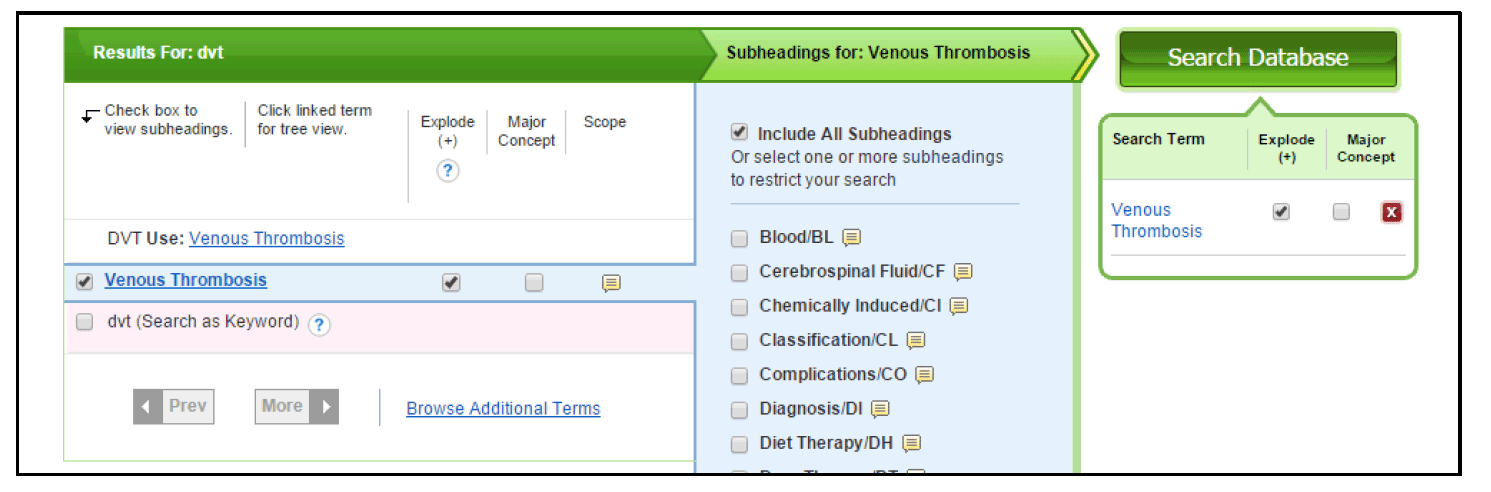
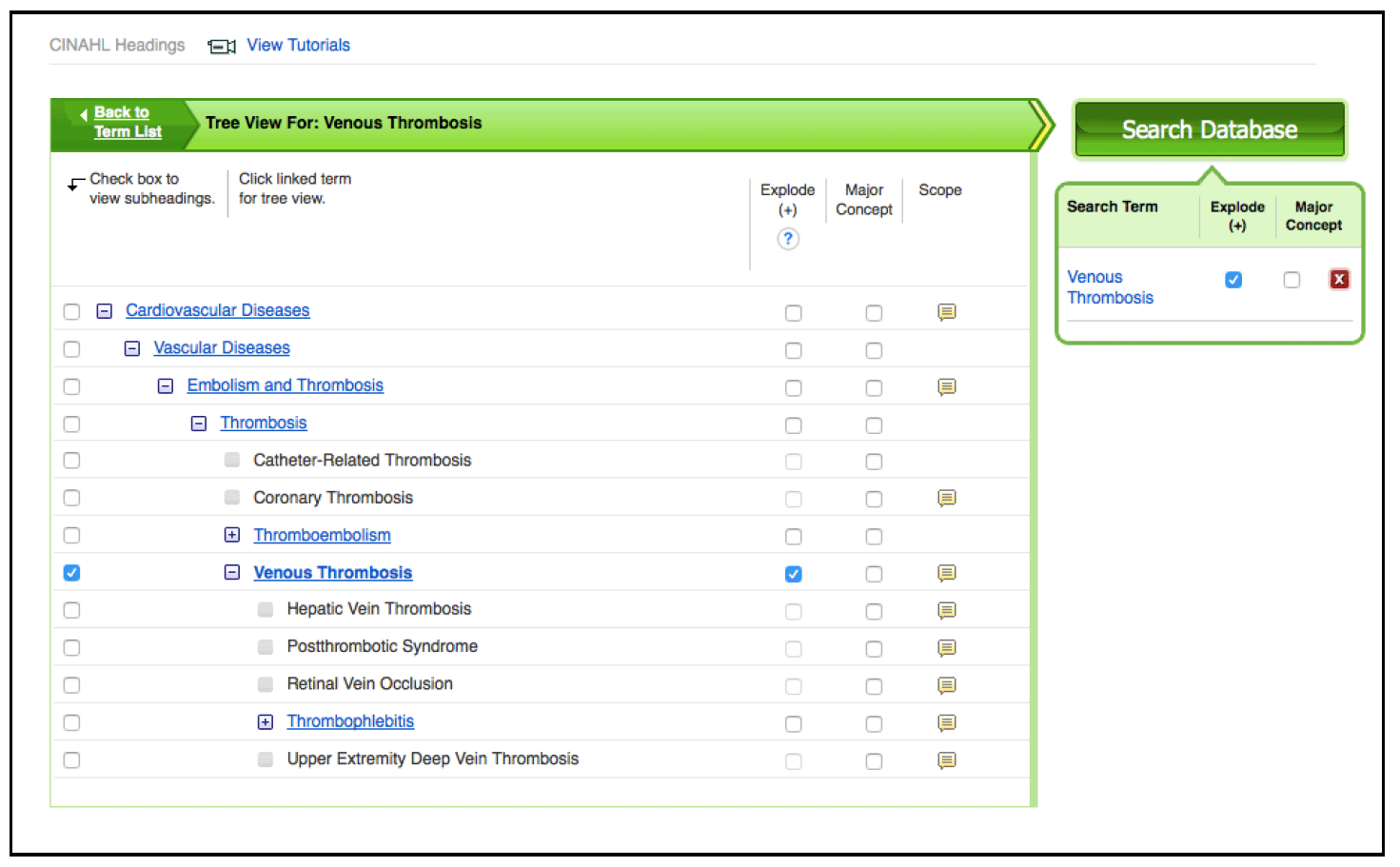
Click on the hyperlinked term Venous Thrombosis to see where the term lies in the thesaurus tree.
The term is automatically ‘exploded’ when used in a search. This means that all the terms underneath are also used to search the database as well
The second concept – compression stockings maps to Compression Garments. Search using this term. There are no other subject headings beneath it so the database does not automatically explode the term

Finally combine the two terms together with a Boolean [AND] to focus the search, apply limiters as the last step and review the search results.

Search multiple EBSCO databases based in your subject area.
Need help? Check out our EBSCO help guide.
A collection of evidence-based resources designed to assist in the clinical decision-making process and to support best practice. Now available through Ovid databases.
Need help? Check out our Joanna Briggs help guide.
Provides authoritative information on medicine, nursing, dentistry, veterinary medicine, the health care system, pre-clinical sciences, etc.
Need help? Check out our EBSCO help guide.
Broad collection for Nursing, includes some Children's Development and all major subject areas of health with qualitative research.
Need help? Check out our Sage help guide.
Nursing and Early Childhood scholarly journals. Choose to search "subscribed journals" only for best results.
Need help? Check out our Science Direct help guide.